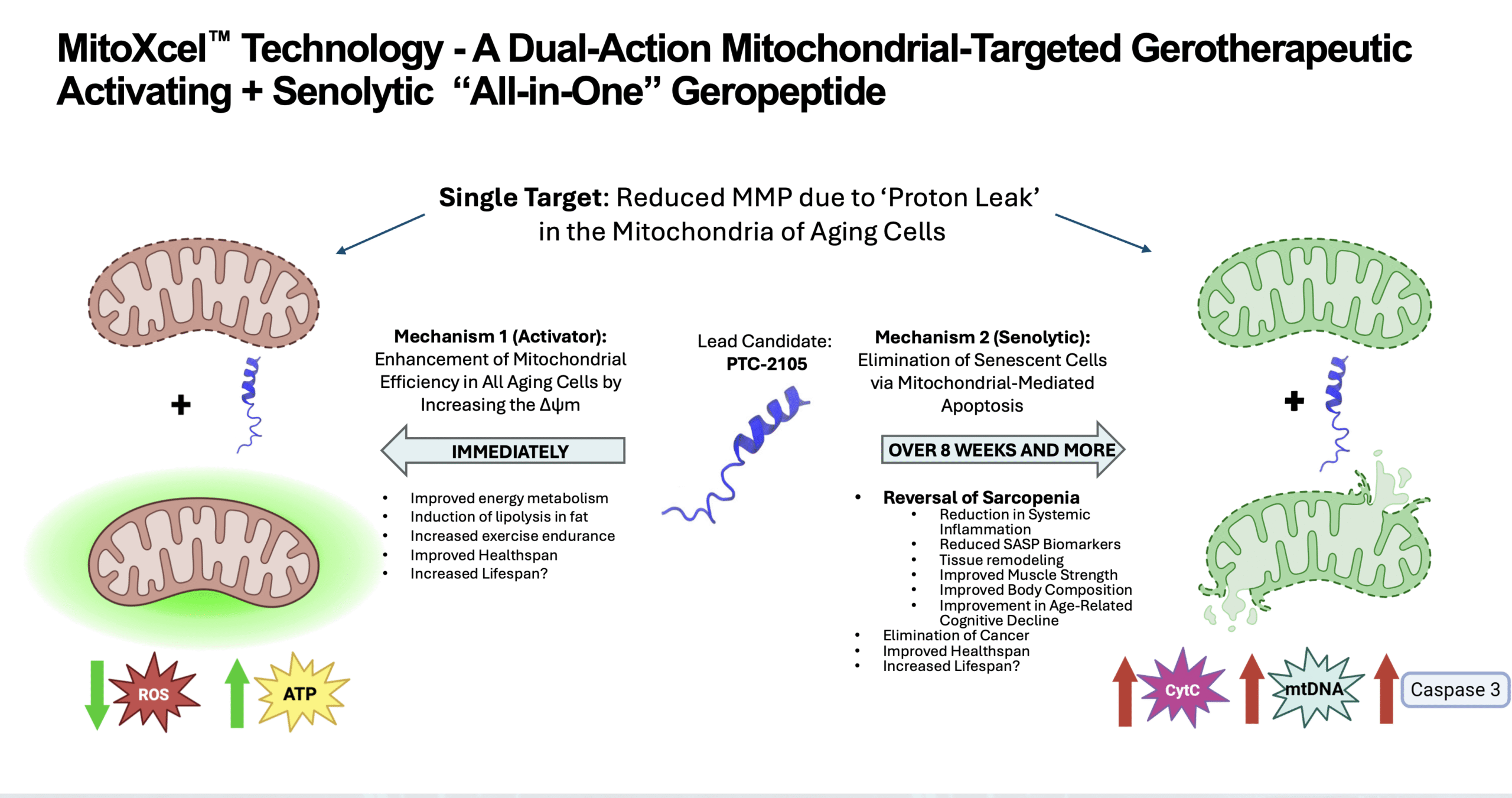
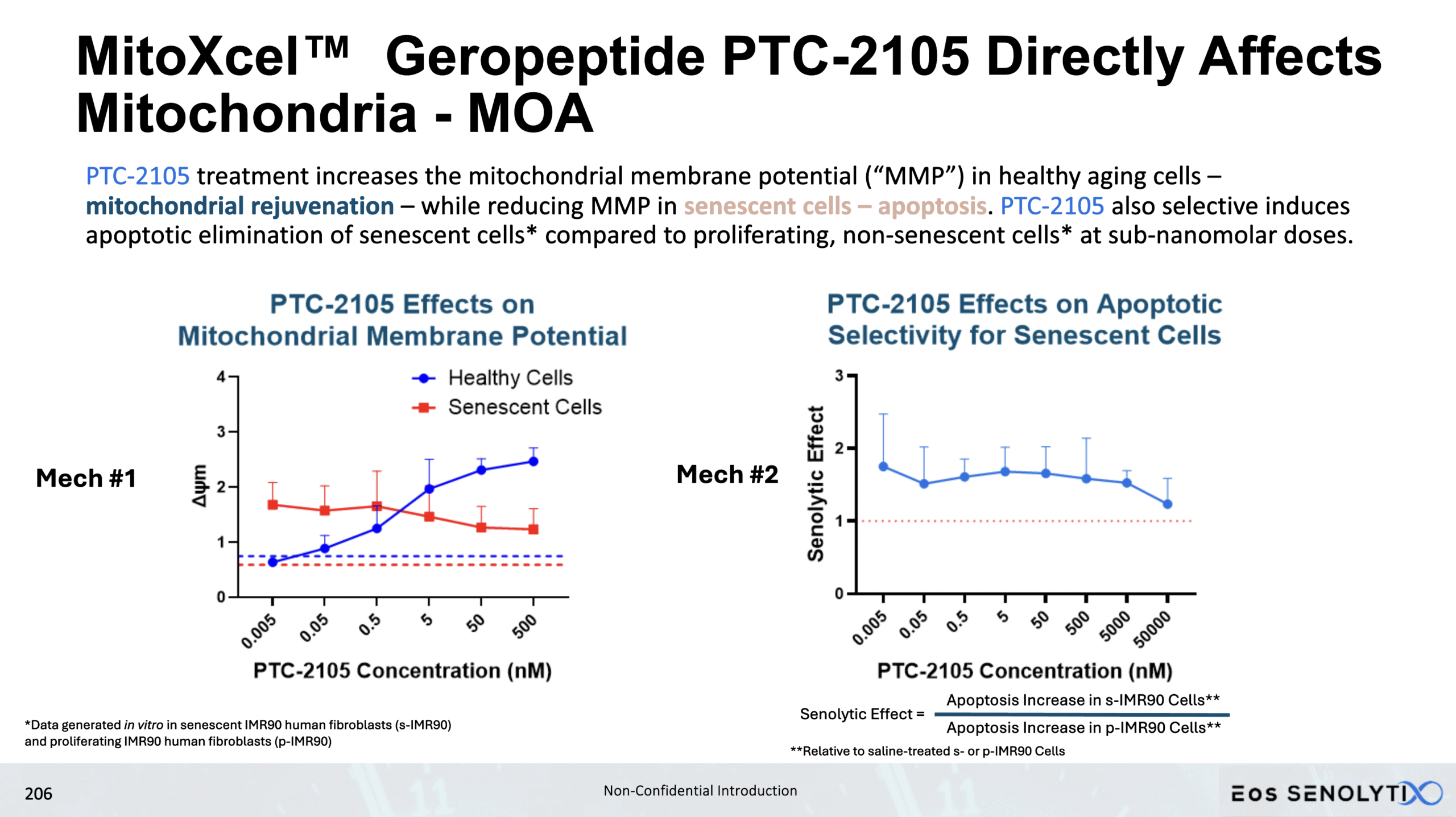
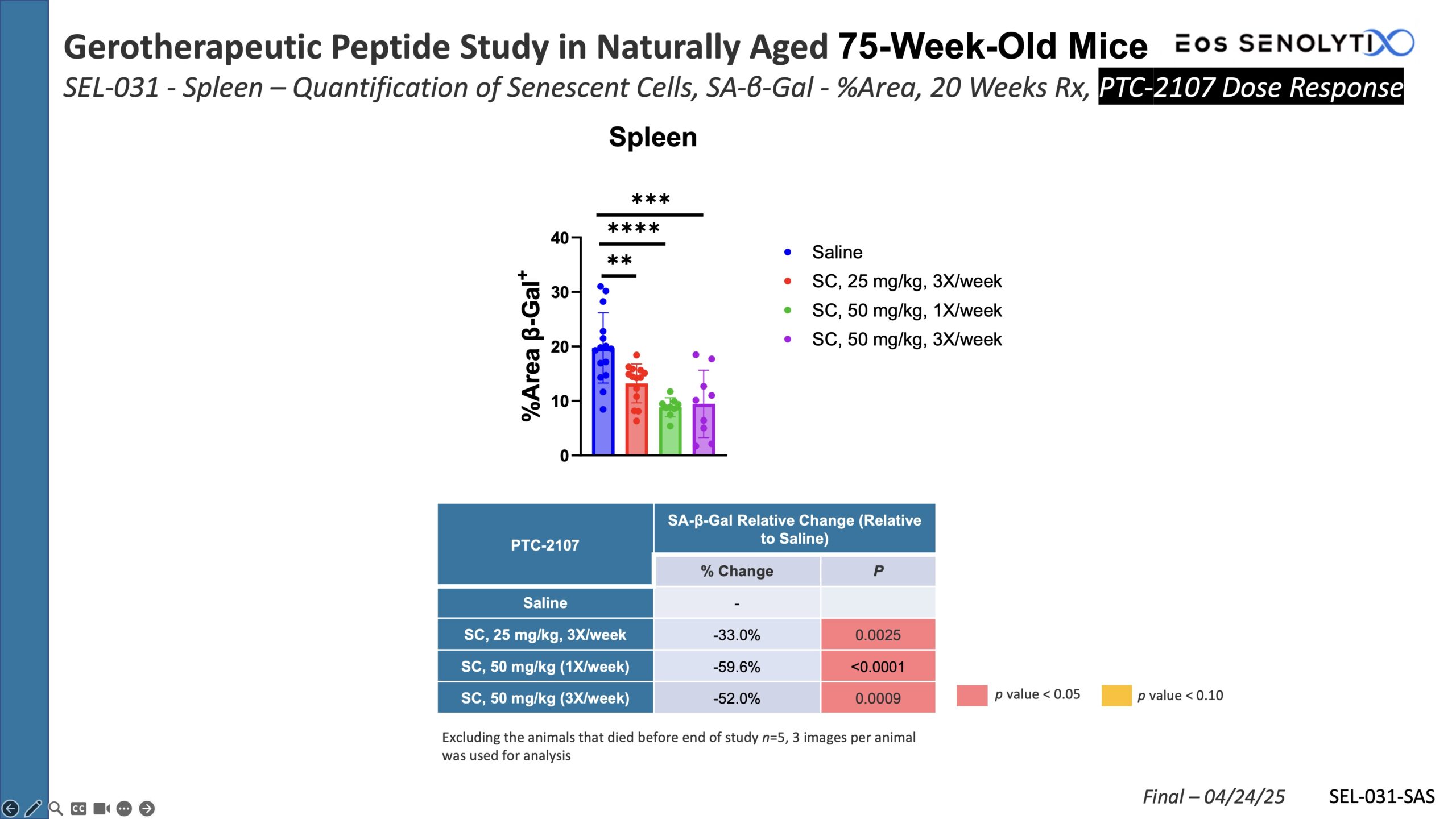
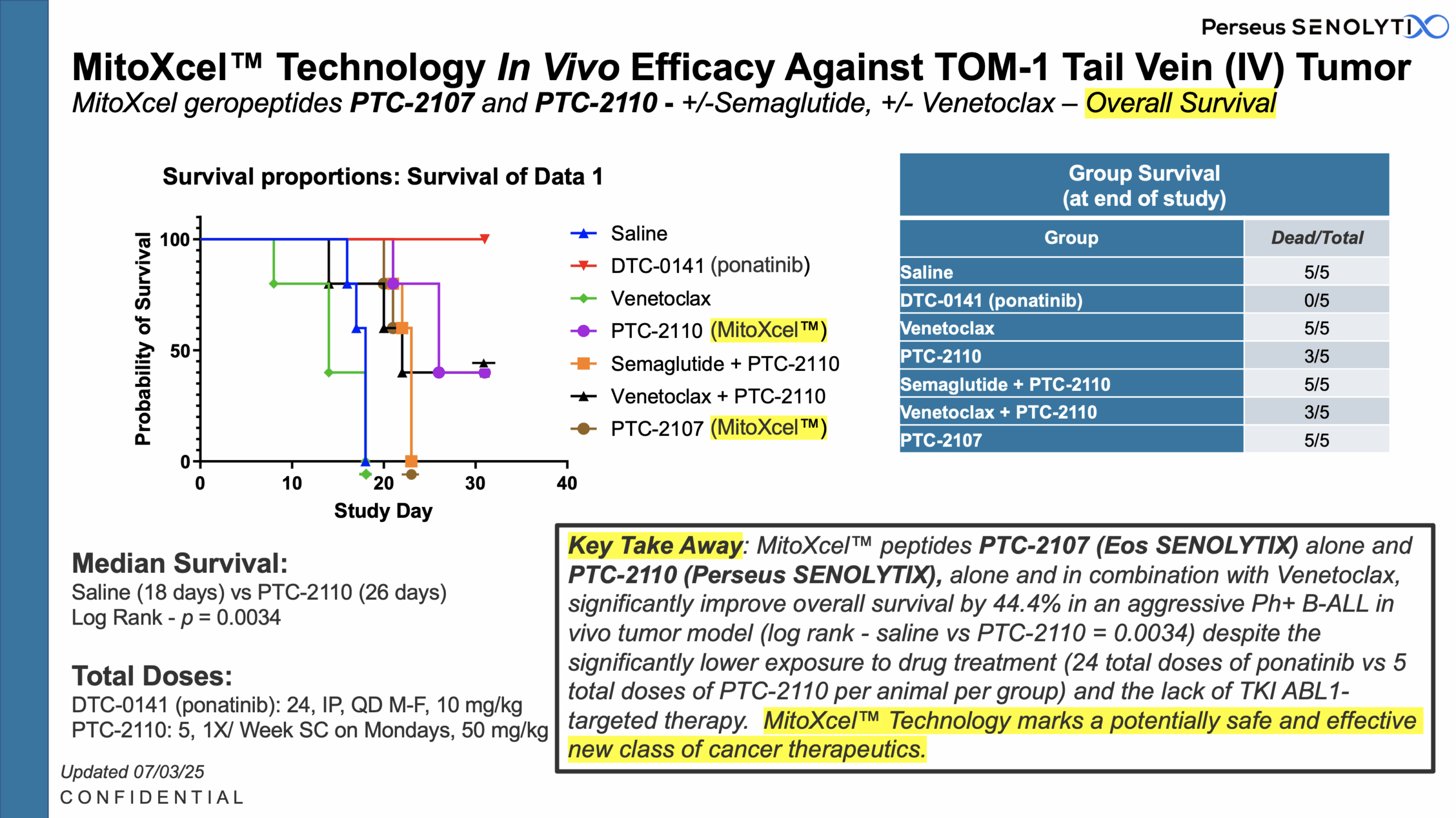
Our MitoXcel™ oncopeptides, clinical candidates PTC-2109, PTC-2110, PTC-2117 and PTC-2128, are:
-
18- to 30-amino acids in length
-
Cross the blood brain barrier
-
Administered via SC injection over an 8-16 week course of treatment in pre-clinical models
Key findings:
-
Selective Elimination of Senescent Cells: In all organs of the body, including the brain, in a dose dependent manner
-
Reduced Systemic Inflammation: Significant decrease in SASP biomarkers
-
Tissue Remodelling to a Healthier Phenotype in Muscle and Fat: Improved body composition including a reduction in fat but an increase in lean body and bone mass
-
Improved Physical Health: Enhanced metabolism, muscle strength, and exercise endurance.
-
Cognitive Benefits: Improved memory and motor coordination.
-
Dose Response Curve Demonstrated
-
Safety Profile: Without demonstrable evidence of toxicity at >40X the efficacious dose after more than 20 weeks of continuous dosing. Normal liver enzyme levels and no adverse effects observed.
Mechanism of Action: Selectively Target the Mitochondria in Senescent, Non-Senescent Cells, and Cancer Cells
-
Completely novel, aging-specific mechanism of action
-
Two key mechanisms, both targeting the Inner Mitochondrial Membrane Potential (Δψm)
-
Validated in three species: human (in vitro), mouse (in vivo) and C. elegans (in vivo)